手把手教你使用Electron9+vue3开发跨平台桌面应用
Electron 是一个基于 chromium 和 nodejs,可以使用 HTML、CSS、和 JavaScript 构建跨平台应用的技术框架,兼容 Mac、Windows 和 Linux。虽然 B/S 是膜前开发 ad 主流,但是 C/S 仍然有很大的市场需求。
受限于浏览器的沙盒限制,网页应用在无法满足某些场景下的使用需求,而桌面应用可以读写本地文件、调用更多系统资源,加上 web 开发成本低、效率高的优势,这种方式越来越收到开发者的喜爱。
本文一步一步教你如何使用 electron9 和 Vue-cli3(vue3.0)在完全保留 Vue 开发 web 应用的习惯下,搭建桌面应用。
本文不涉及 electron 和 Vue 的开发教程,仅以实现两者结合为目的,如需深入学习 electron 和 Vue,请访问官方:
- Electron: https://electronjs.org/
- vue: https://cn.vuejs.org/
- vue-cli: https://cli.vuejs.org/zh/
- stylus: http://stylus-lang.com/
学习本文前,你需要提前掌握以下技能:
HTML、CSS、JavaScript、vue
※注:本文代码区域每行开头的“+”表示新增,“-”表示删除,“M”表示修改;代码中的“...”表示省略。
先看看通过本教程能学到什么。
目录
1 创建项目
1.1 使用 cnpm 加速下载
1.2 为什么不使用 SimulatedGREG/electron-vue
1.3 安装/升级 vue-cli3
1.4 创建 vue 项目
1.5 自动安装 electron
1.6 手动安装 electron
1.7 编译并启动 APP
2 配置项目
2.1 配置 ESLint 代码格式检查工具
2.2 配置 vue
3 项目基本设定
3.1 主进程和渲染进程简介
3.2 APP 窗口大小
3.3 取消跨域限制
3.4 取消菜单栏
3.5 设置 APP 窗口图标
3.6 设置 APP 窗口标题栏名称
4 build 最终产品
4.1 设置 APP 及安装包图标
4.2 设置 APP 名称
4.3 打包 APP
4.4 可能出现的错误
5 关于项目开发的一些经验
5.1 src 目录结构参考
5.2 换肤功能的实现
5.3 从 Electron4.x 升级到 5.x
5.4 注册快捷键打开 devTools
1 创建项目
1.1 使用淘宝镜像源加速下载
npm 有时下载速度很慢,可以安装 cnpm,从国内淘宝镜像下载,执行以下命令:
npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
以后 npm 直接替换成 cnpm 使用。
以上是根据开发者的喜好选择,也可以继续使用yarn 或者npm
npm config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org或者
yarn config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org国内用户尽量更换为国内镜像源,electron 体积较大很多朋友在使用 npm 源的时候经常下载失败
1.2 为什么不使用 SimulatedGREG/electron-vue
SimulatedGREG/electron-vue 已经很久没有更新了,而且其生成的工程结构并不是 vue-cli3。所以放弃使用。
1.3 安装/升级 vue-cli3
先执行以下命令,确认下本地安装的 vue-cli 版本:
vue -V在写本文时,我使用的是 4.5.9 版本。
如果本地使用的是 vue-cli2.x 或者更早版本,可先卸载:
cnpm uninstall vue-cli -g※注:vue-cli3 使用了新的 npm 包名,与旧版本不一样。
如果还没有安装 vue-cli3,先执行以下命令安装:
cnpm install @vue/cli -g如果你已安装vue-cli3,但不是最新版本,可执行以下命令升级:
(我这里使用 cnpm 并没有完成升级,所以使用了 npm)
npm update @vue/cli -g1.4 创建 vue 项目
找个喜欢的目录,执行以下命令,创建 vue 项目:
(这里把项目名称定为 electron-vue-demo)
vue create electron-vue-demo会出现以下选项(如果熟悉此步骤可跳过本节内容):
Vue CLI v4.5.9
? Please pick a preset:
Default ([Vue 2] babel, eslint)
Default (Vue 3 Preview) ([Vue 3] babel, eslint)
❯ Manually select features
选择“Manually select features” (自定义安装)。
? Check the features needed for your project:
◉ Choose Vue version
◉ Babel
◉ TypeScript
◉ Progressive Web App (PWA) Support
◉ Router
❯◉ Vuex
◉ CSS Pre-processors
◉ Linter / Formatter
◯ Unit Testing
◯ E2E Testing这里选择了常用的模块,请根据实际需求进行选择。
? Choose a version of Vue.js that you want to start the project with
2.x
❯ 3.x (Preview)
这里我们选择最新版 Vue3.0 来开发
? Use class-style component syntax? (y/N)是否使用类写法,这里默认 N
? Use Babel alongside TypeScript (required for modern mode, auto-detected polyfi
lls, transpiling JSX)? Yes是否使用适用于 typescript 的 bable:Y
? Use history mode for router? (Requires proper server setup for index fallback
in production) Yes如果选择了 router,这里会询问是否使用 history 模式。
vue-router 默认使用 hash 模式(即通过 url#hash 来跳转页面),使用 URL 的 hash 来模拟一个完整的 URL,当 URL 改变时,页面不会重新加载。 如果使用 history,URL 就像正常的 url,例如 http://yoursite.com/user/id ,比较好看。但是还需要后台配置支持。
? Pick a CSS pre-processor (PostCSS, Autoprefixer and CSS Modules are supported
by default):
Sass/SCSS (with dart-sass)
Sass/SCSS (with node-sass)
❯ Less
Stylus选择 CSS 预处理模块,这里我们使用“Less”。
? Pick a linter / formatter config: (Use arrow keys)
ESLint with error prevention only
ESLint + Airbnb config
❯ ESLint + Standard config
ESLint + Prettier选择 ESLint 代码格式检查工具的配置,选择“ESLint + Standard config”,标准配置。
? Pick additional lint features: (Press <space> to select, <a> to toggle all, <i
> to invert selection)
❯◉ Lint on save
◯ Lint and fix on commit
Line on save 表示在保存代码的时候,进行格式检查。
Lint and fix on commit 表示在 git commit 的时候自动纠正格式。
这里只选择“Lint on save”。
? Where do you prefer placing config for Babel, PostCSS, ESLint, etc.?
In dedicated config files
❯ In package.json这里问把 babel, postcss, eslint 这些配置文件放哪?
In dedicated config files 表示独立文件
In package.json 表示放在 package.json 里
? Save this as a preset for future projects? (y/N) N是否为以后的项目保留这些设置?选择“N”。
然后耐心等待项目安装完成。
1.5 自动安装 electron
※注:此过程可能需要科学上网,由于直接从国外镜像下载较慢,可能需要等待很漫长的时间。如果你对自己的网速没有超强自信,请跳过本节,前往 1.6 小节手动安装。
进入到项目根目录,执行:
vue add electron-builder在安装过程中,很可能会卡在这一步不动了:
node ./download-chromedriver.js
没关系,我们先强制结束掉。再执行一次vue add electron-builder,然后就可以顺利通过了。
接下来出现配置选项:
✨ Done in 7.73s.
✔ Successfully installed plugin: vue-cli-plugin-electron-builder
? Choose Electron Version (Use arrow keys)
^7.0.0
^8.0.0
❯ ^9.0.0
选择 Electron 版本。选择 “^9.0.0”。
然后耐心等待安装完成。如果中间出现错误中断了,请重复此步骤。
安装完成后会自动在 src 目录下生成background.ts并修改了package.json。
※注:由于网络原因,如果中间出现过中断失败,再次重新安装可能会很快完成,但实际上 electron 可能并未安装完全。建议完成以上步骤后,直接删除项目根目录的 node_modules/,并且执行 cnpm install,从国内镜像重新安装所有依赖包。
1.6 手动安装 electron
※注:如果已经通过 1.5 章节的操作,请直接跳过本小节。
修改 package.json,添加以下 7 行:
...
"scripts": {
"serve": "vue-cli-service serve",
"build": "vue-cli-service build",
"lint": "vue-cli-service lint",
+ "electron:build": "vue-cli-service electron:build",
+ "electron:serve": "vue-cli-service electron:serve",
+ "postinstall": "electron-builder install-app-deps",
+ "postuninstall": "electron-builder install-app-deps"
},
+ "main": "background.js",
"dependencies": {
"core-js": "^2.6.5",
"vue": "^2.6.6",
"vue-router": "^3.0.1",
"vuex": "^3.0.1"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@vue/cli-plugin-babel": "^3.8.0",
"@vue/cli-plugin-eslint": "^3.8.0",
"@vue/cli-service": "^3.8.0",
"@vue/eslint-config-standard": "^4.0.0",
"babel-eslint": "^10.0.1",
+ "electron": "^9.0.0",
+ "electron-devtools-installer": "^3.1.0",
"eslint": "^5.16.0",
"eslint-plugin-vue": "^5.0.0",
"stylus": "^0.54.5",
"stylus-loader": "^3.0.2",
+ "vue-cli-plugin-electron-builder": "~2.0.0-rc.5",
"vue-template-compiler": "^2.6.10"
},
...新建 src/background.js
在 src 目录下新建background.js,复制以下代码:
'use strict'
import { app, protocol, BrowserWindow } from 'electron'
import { createProtocol } from 'vue-cli-plugin-electron-builder/lib'
import installExtension, { VUEJS_DEVTOOLS } from 'electron-devtools-installer'
const isDevelopment = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'
// Scheme must be registered before the app is ready
protocol.registerSchemesAsPrivileged([
{ scheme: 'app', privileges: { secure: true, standard: true } }
])
async function createWindow () {
// Create the browser window.
const win = new BrowserWindow({
width: 800,
height: 600,
webPreferences: {
// Use pluginOptions.nodeIntegration, leave this alone
// See nklayman.github.io/vue-cli-plugin-electron-builder/guide/security.html#node-integration for more info
nodeIntegration: (process.env
.ELECTRON_NODE_INTEGRATION as unknown) as boolean
}
})
if (process.env.WEBPACK_DEV_SERVER_URL) {
// Load the url of the dev server if in development mode
await win.loadURL(process.env.WEBPACK_DEV_SERVER_URL as string)
if (!process.env.IS_TEST) win.webContents.openDevTools()
} else {
createProtocol('app')
// Load the index.html when not in development
win.loadURL('app://./index.html')
}
}
// Quit when all windows are closed.
app.on('window-all-closed', () => {
// On macOS it is common for applications and their menu bar
// to stay active until the user quits explicitly with Cmd + Q
if (process.platform !== 'darwin') {
app.quit()
}
})
app.on('activate', () => {
// On macOS it's common to re-create a window in the app when the
// dock icon is clicked and there are no other windows open.
if (BrowserWindow.getAllWindows().length === 0) createWindow()
})
// This method will be called when Electron has finished
// initialization and is ready to create browser windows.
// Some APIs can only be used after this event occurs.
app.on('ready', async () => {
if (isDevelopment && !process.env.IS_TEST) {
// Install Vue Devtools
try {
await installExtension(VUEJS_DEVTOOLS)
} catch (e) {
console.error('Vue Devtools failed to install:', e.toString())
}
}
createWindow()
})
// Exit cleanly on request from parent process in development mode.
if (isDevelopment) {
if (process.platform === 'win32') {
process.on('message', (data) => {
if (data === 'graceful-exit') {
app.quit()
}
})
} else {
process.on('SIGTERM', () => {
app.quit()
})
}
}
以上代码是 1.5 小节使用自动化方式安装后生成的。
安装依赖包
在项目根目录执行,安装全部依赖包:
cnpm install如果安装过程中报错:Error: post install error, please remove node_modules before retry!可以忽略,不影响后续使用。
1.7 编译并启动 APP
执行以下命令,开始编译 APP,并启动开发环境 APP:
npm run electron:serve首次启动可能会等待很久,出现以下信息:
INFO Launching Electron...
Failed to fetch extension, trying 4 more times
Failed to fetch extension, trying 3 more times
Failed to fetch extension, trying 2 more times
...这是因为在请求安装vuejs devtools插件。需要科学上网才能安装成功。如果不能科学上网也没关系,耐心等待 5 次请求失败后会自动跳过。
编译成功后,就会出现开发环境的 APP 了。
Mac 测试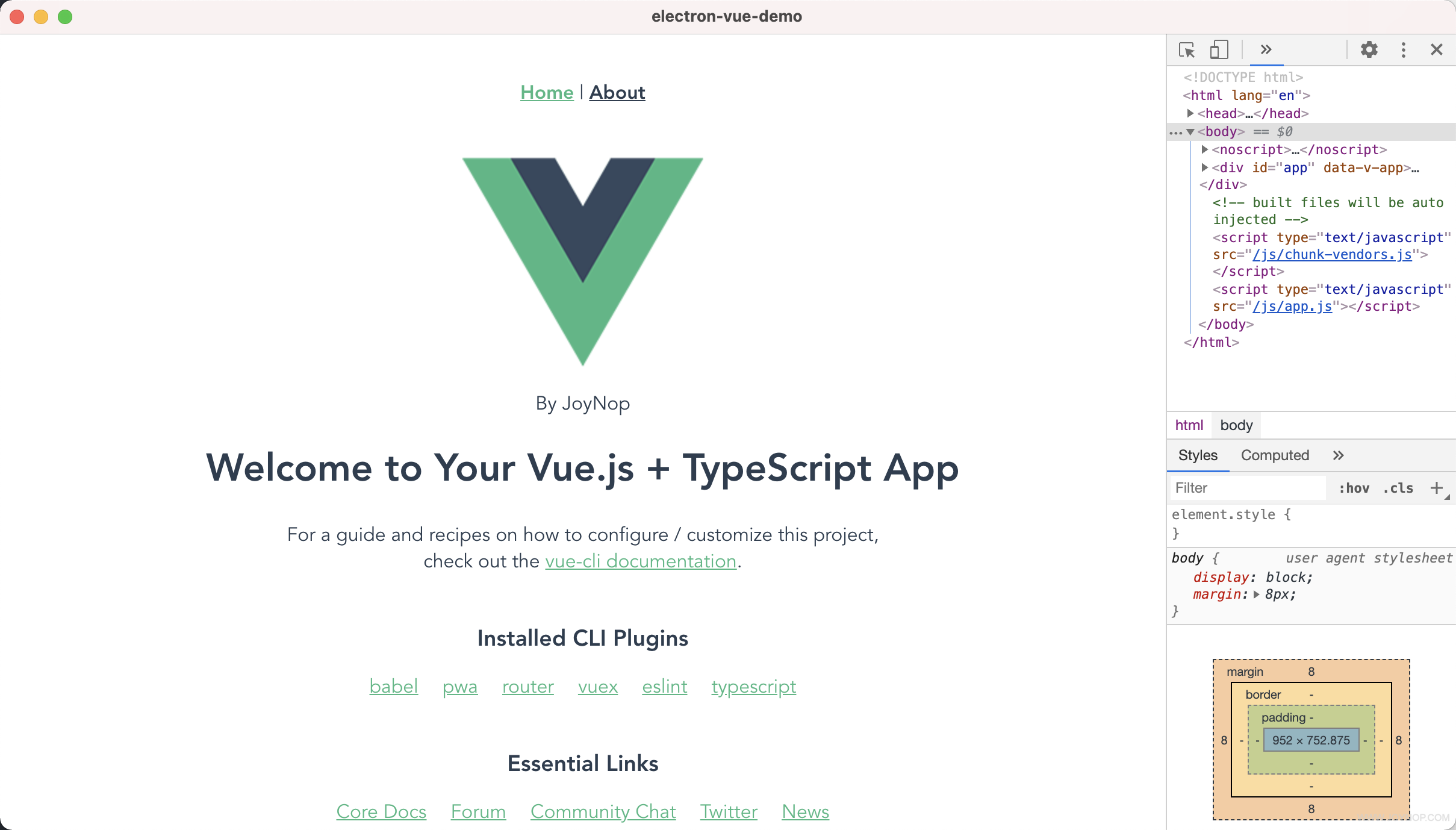
2 配置项目
2.1 配置 ESLint 代码格式检查工具
ESlint 可以高效的检查代码格式,让参与项目的所有工程师都能保持统一的代码风格。其检测精度甚至可以精确到是否多一个空格或者少一个空格。代码格式的统一对提高团队的协同开发效率有很大的帮助,特别是对有代码洁癖的工程师。
在项目根目录下创建.eslintrc.js (注意文件名前面有个“.”)
请粘贴以下代码:
module.exports = {
root: true,
env: {
node: true,
},
extends: ["plugin:vue/essential", "@vue/standard"],
rules: {
"no-debugger": process.env.NODE_ENV === "production" ? "error" : "off",
// 不检测语句末尾的分号
semi: ["off", "always"],
// 强制缩进为2个空格
indent: ["error", 2],
// 关闭函数名称跟括号之间的空格检测
"space-before-function-paren": 0,
// 忽略大括号内的空格
"object-curly-spacing": 0,
},
parserOptions: {
parser: "babel-eslint",
},
};这里说明下关于 indent 缩进的配置,要配合项目根目录下的.editorconfig
[*.{js,jsx,ts,tsx,vue}]
indent_style = space <--这里定义缩进类型是空格还是tab
indent_size = 2 <--这里需要与.eslintrc.js的indent对应
trim_trailing_whitespace = true
insert_final_newline = true
.editorconfig 用于 IDE 自动格式化代码
.eslintrc.js 用于 ESlint 检测
2.2 配置 vue
在项目根目录下创建 vue.config.js,粘贴以下代码:
const path = require("path");
function resolve(dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, dir);
}
module.exports = {
publicPath: "./",
devServer: {
// can be overwritten by process.env.HOST
host: "0.0.0.0",
port: 8080,
},
chainWebpack: (config) => {
config.resolve.alias
.set("@", resolve("src"))
.set("src", resolve("src"))
.set("common", resolve("src/common"))
.set("components", resolve("src/components"));
},
};devServer 用于设置开发环境的服务,这里表示在本地 8080 端口启动 web 服务。
chainWebpack 我们给项目目录起了“别名(alias)”,在代码中,我们可以直接用“别名”访问资源,省去了每次输入完整相对路径的麻烦。
※注:
◉ 在 js 代码中可直接使用别名,例如:
@/common/js/xxx.js 等价于 src/common/js/xxx.js
common/js/xxx.js 等价于 src/common/js/xxx.js
◉ 在 css 或者 html 中使用别名,需要在别名前加“~”,例如:
@import "~common/stylus/font.styl";
3 项目基本设定
3.1 主进程和渲染进程简介
在开始下面的步骤之前,很有必要简单了解下 Electron 的应用架构。
主进程
Electron 运行 package.json 的 main 脚本(background.js)的进程被称为主进程。 在主进程中运行的脚本通过创建 web 页面来展示用户界面。 一个 Electron 应用总是有且只有一个主进程。
渲染进程
由于 Electron 使用了 Chromium 来展示 web 页面,所以 Chromium 的多进程架构也被使用到。 每个 Electron 中的 web 页面运行在它自己的渲染进程中。
在普通的浏览器中,web 页面通常在一个沙盒环境中运行,不被允许去接触原生的资源。 然而 Electron 的用户在 Node.js 的 API 支持下可以在页面中和操作系统进行一些底层交互。
主进程与渲染进程的关系
主进程使用 BrowserWindow 实例创建页面。 每个 BrowserWindow 实例都在自己的渲染进程里运行页面。 当一个 BrowserWindow 实例被销毁后,相应的渲染进程也会被终止。
主进程管理所有的 web 页面和它们对应的渲染进程。 每个渲染进程都是独立的,它只关心它所运行的 web 页面。
3.2 APP 窗口大小
修改 background.js:
function createWindow () {
// Create the browser window.
win = new BrowserWindow({
M width: 1200,
M height: 620,
webPreferences: {
nodeIntegration: true
}
})3.3 取消跨域限制
修改 background.js:
function createWindow () {
// Create the browser window.
win = new BrowserWindow({
width: 1200,
height: 620,
webPreferences: {
+ webSecurity: false,
nodeIntegration: true
}
})3.4 取消菜单栏
在我们生成的桌面 APP 中,我们可以看到默认的菜单栏。
在 windows 中,菜单栏在 APP 窗口内的顶部;在 macOS 中,菜单栏位于电脑屏幕顶部。
为了方便项目将来也能直接生成纯 web 应用,尽量把 APP 的全部功能都做到渲染进程里,这里我们取消菜单栏。
由于 macOS 的特殊性,顶部菜单栏无法删除,所以我们针对 macOS 特殊处理,把菜单栏只保留“关于”和“退出”。
修改 background.js:
M import { app, protocol, BrowserWindow, Menu } from 'electron'
...
function createWindow () {
...
win.on('closed', () => {
win = null
})
+ createMenu()
}
+ // 设置菜单栏
+ function createMenu() {
+ // darwin表示macOS,针对macOS的设置
+ if (process.platform === 'darwin') {
+ const template = [
+ {
+ label: 'App Demo',
+ submenu: [
+ {
+ role: 'about'
+ },
+ {
+ role: 'quit'
+ }]
+ }]
+ let menu = Menu.buildFromTemplate(template)
+ Menu.setApplicationMenu(menu)
+ } else {
+ // windows及linux系统
+ Menu.setApplicationMenu(null)
+ }
+ }macOS 菜单栏名称 label 的“App Demo”会在 build 版本生效,dev 版本会显示“Electron”。
3.5 设置 APP 窗口图标
准备 windows 和 macOS 两版图标。
windows: app.ico 最小尺寸:256x256
macOS: app.png 或 app.icns 最小尺寸:512x512 (后续 4.1 章节用到)
把图标文件放到 public/目录下,项目结构如下:
|- /dist_electron
(略)
|- /public
|- app.icns <-- 本教程暂时未使用icns
|- app.ico
|- app.png
|- favicon.ico
|- index.html
|- /src
(略)
|- .editorconfig
|- .eslintrc.js
|- .gitignore
|- babel.config.js
|- package.json
|- package-lock.json
|- README.md
可以顺便把 favicon.ico 也修改一下,但是在桌面版 APP 上是用不到的。如果以后生成纯 web 项目才会用到。
修改 background.js,让 APP 窗口应用图标:
function createWindow () {
// Create the browser window.
win = new BrowserWindow({
width: 1200,
height: 620,
webPreferences: {
nodeIntegration: true
},
+ // eslint-disable-next-line no-undef
+ icon: `${__static}/app.ico`
})
这里的${__static}对应的是public目录
现在,Windows 系统上可以看到开发环境的 APP 窗口图标已经生效了。
macOS 图标请参照 4.1 章节,并且需要在 build 后才能生效。
3.6 设置 APP 窗口标题栏名称
修改 public/index.html:
我们把 electron-vue-demo 改为 App Demo。
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico" />
M
<title>App Demo</title>
</head>4 build 最终产品
这里我们已经集成了 electron-builder 工具,官方文档可以参阅:https://www.electron.build/
4.1 设置 APP 及安装包图标
在 3.5 章节,我们的图标生效于运行 APP 的窗口。本小节将生效于最终生成的可执行文件和安装包图标。需要准备的图标文件请回看 3.5 章节。
修改vue.config.js
chainWebpack: config => {...},
+ pluginOptions: {
+ electronBuilder: {
+ builderOptions: {
+ win: {
+ icon: './public/app.ico'
+ },
+ mac: {
+ icon: './public/app.png'
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
...运行 build 后的 mac 版本,可以看到图标都已生效了。
安装包和可执行文件的截图就不再放出了。
4.2 设置 APP 名称
APP 名称包括安装包中 APP 的名称、可执行文件的文件名。
修改 vue.config.js:
pluginOptions: {
electronBuilder: {
builderOptions: {
win: {
icon: './public/app.ico'
},
mac: {
icon: './public/app.png'
},
+ productName: 'AppDemo'
}
}
}
4.3 打包 APP
执行以下命令,可以 build 工程:
npm run electron:build
最终在dist_electron目录下生成 build 后的产品。
windows版本
目录如下:
/dist_electron
|- /bundled
(略)
|- /win-unpacked <-- 绿色版
(略)
|- AppDemo Setup 0.1.0.exe <-- 安装文件
|- AppDemo Setup 0.1.0.exe.blockmap
|- builder-effective-config.yaml
|- index.js这里其实就win-unpacked和AppDemo Setup 0.1.0.exe有用。
※注:在32位环境下打包生成的是32位APP,在64位环境下打包生成的是64位APP。
mac版本
/dist_electron
|- /bundled
(略)
|- /mac
|- AppDemo <-- 绿色版
|- AppDemo-0.1.0-mac.zip <-- 绿色版压缩包
|- AppDemo-0.1.0-mac.dmg <-- 安装包
|- AppDemo-0.1.0.dmg.blockmap
|- builder-effective-config.yaml
|- index.js
4.4 可能出现的错误
我曾经在Win10 64bit 1809版本上build失败,保存信息中提示:
Error output:
Can't open output file
Error - aborting creation process与此同时,在win7和win10 1803版本build正常。经研究,无果。后来把windows升级到1903版本,问题解决了。应该是vue-cli-plugin-electron-builder插件与系统之间的问题导致。
5 关于项目开发的一些经验
在完成以上章节后,后面基本可以完全按照web方式开发了。这里简单分享下一些小经验。
5.1 src目录结构参考
/src
|- /common
|- /fonts
|- /images
|- /js
|- api
|- libs
|- /stylus
|- /components
|- /base
|- /modules
|- /moduleA
|- /moduleB
...
|- /views
|- App.vue
|- background.js
|- main.js
|- router.js
|- store.js
下面对部分重要目录简要说明:
common/ - 项目公用库
common/fonts/ - 字体文件
common/images/ - 公用图片
common/js/ - 公用js目录
common/js/api/ - 把api按类别封装成函数,并export出去,减少业务逻辑中的重复代码
common/js/lib/ - 存放一些公用函数库、定义的常量库等
common/stylus/ - Stylus样式文件
components/ - vue组件目录
component/base/ - vue基础组件,例如自定义的CheckBox、日期选择器、Dialog、Toaster、分页组件等
component/modules/ - vue模块
views/ - vue页面
5.2 换肤功能的实现
很多项目都有实时换肤的需求,在实际开发中,虽然我们使用了Sass、Less、Stylus等高端样式工具,但最终经过编译还是要回归到最原始的CSS。换肤的本质还是实时替换皮肤样式文件。
失败案例
以Stylus为例,抽象出皮肤文件skin.styl:
$color-bg = #fff
$color-text = #333
在业务样式中引用:
@import 'skin.styl'
body
background: $color-bg
color: $color-text当经过编译后,生成的css为:
body {background: #fff; color: #333;}
样式已经写死了,无法换肤。
那么应该怎么做呢?
成功案例
项目根目录下的public目录是静态目录,也就是说在build最终产品的时候,它里面的文件将原封不动保留。所以,可以将皮肤文件放在这里。
|- /public
+ |- /skin
+ |- /skin01
+ |- skin.css
+ |- /skin02
+ |- skin.css
|- app.icns
|- app.ico
|- app.png
|- favicon.ico
|- index.html由于Electron的是基于chromium内核,所以不用担心代码的浏览器兼容问题。接下来就是发挥CSS3变量var(--*)的时候了。
public/skin/skin01/skin.css:
:root {
--color-bg: #fff;
--color-text: #333;
}
public/skin/skin02/skin.css:
:root {
--color-bg: #263238;
--color-text: #b2ccd6;
}修改src/App.vue:
...
<style lang="stylus">
+ body
+ background: var(--color-bg)
+ color: var(--color-text)
#app
font-family 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif
-webkit-font-smoothing antialiased
-moz-osx-font-smoothing grayscale
text-align center
M color: var(--color-text)
#nav
padding 30px
a
font-weight bold
M color: var(--color-text)
&.router-link-exact-active
color #42b983
</style>在public/index.html引入皮肤样式,注意加上id="app-skin":
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico">
+ <link rel="stylesheet" href="<%= BASE_URL %>skin/skin01/skin.css" id="app-skin">
<title>App Demo</title>
</head>篇幅有限,这里就不写通过js修改皮肤的代码了。
5.3 注册快捷键打开devTools
在Electron中打开devTools是通过主线程中调用win.webContents.openDevTools()实现的。以上教程仅在开发环境初始启动的时候打开devTools,但是一旦关闭就不能再打开了。下面讲一下怎么通过快捷键打开devTools。
修改background.js:
...
M import { app, protocol, BrowserWindow, Menu, globalShortcut } from 'electron'
...
app.on('ready', async () => {
if (isDevelopment && !process.env.IS_TEST) {
// Install Vue Devtools
try {
await installVueDevtools()
} catch (e) {
console.error('Vue Devtools failed to install:', e.toString())
}
}
// 在开发环境和生产环境均可通过快捷键打开devTools
+ globalShortcut.register('CommandOrControl+Shift+i', function () {
+ win.webContents.openDevTools()
+ })
createWindow()
})
在windows下,按Ctrl+Shift+i即可打开devTools
在macOS下,按Commond+Shift+i即可打开devTools
为什么没用F12?因为windows系统中,F12是系统保留快捷键,无法使用。官方原话是这么解释的:
The F12 key is reserved for use by the debugger at all times, so it should not be registered as a hot key. Even when you are not debugging an application, F12 is reserved in case a kernel-mode debugger or a just-in-time debugger is resident.
但是可以使用Ctrl+F12,只要不单独使用F12就可以。
以上代码在开发环境和生产环境中均有效,为保证生产环境的安全,建议不要在生产环境中使用。放到上面的if语句中即可。
本作品采用 知识共享署名-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议 进行许可。
若对文章有疑问,请hi#joynop.com联系博主
 微信
微信 支付宝
支付宝
感谢大佬